A Beginner's Guide to Taiwanese: Difference between revisions
(→Tones: re-insert exception on a) |
|||
| (211 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Lie hør. | [[File:Lie hør.mp3|thumb|"Hello" in Taiwanese, written '''''[[Lie hør!]]''''' in MLT]] | ||
'''''Li | '''''Li hø!''''' [[Taiwanese Hokkien|Taiwanese]] is a beautiful and musical language spoken in [[Taioaan|Taiwan]] and by Taiwanese people around the world. This '''''Beginner's Guide to Taiwanese''''' will provide you with a brief introduction to the spoken language as well as a system for writing Taiwanese called [[Modern Literal Taiwanese]] (MLT), also known as "Modern Taiwanese Language" (MTL). | ||
Most speakers of Taiwanese | Most speakers of Taiwanese aren't aware that there are several writing systems for the language. ''[[Pe̍h-ōe-jī]]'' (POJ), also known as Church Romanization, might be the most popular romanization, though the government is now promoting a similar system called ''[[Tâi-lô]]''. We're going to use MTL here because we found it very useful while studying Taiwanese at the [[Washington DC Taiwanese School]], and we think it could help you too. True, most Taiwanese speakers won't be able to read any of these systems, but they will probably understand you better because you learned one. | ||
== | == How to make a syllable == | ||
Let's learn how to write any syllable using the [[MLT alphabet]]. The three important parts of a syllable we will look at first are: starting consonant, vowel, and ending consonant. We will talk about tones later. | |||
=== | === Initial consonants === | ||
A syllable can start with one of [[Modern Literal Taiwanese alphabet#Consonants|18 initial consonants]]. Some sounds have an approximation in English, while others may be more exotic. For now, you can just ignore the silent indicators (mainly ''f'', ''x'', ''r'', ''v''). | |||
[[File: | [[File:Initial_consonants.mp3|thumb|none|Consonants]] | ||
[[File:initial_consonant_examples.mp3|thumb|none|Examples]] | |||
{{Initial_consonants}} | {{Initial_consonants}} | ||
The ''p'' vs. ''b'' and ''k'' vs. ''g'' may be hard to differentiate at first. They are part of a three-way distinction, going from ''muddy'' to plain to [[Aspirated consonant|aspirated]]. | The ''p'' vs. ''b'' and ''k'' vs. ''g'' may be hard to differentiate at first. They are part of a three-way distinction, going from ''muddy'' to plain to [[Aspirated consonant|aspirated]]. | ||
* | * ''b'' and ''g'' are voiced: the vocal cords vibrate along with the consonant | ||
* | * ''p'', ''t'', ''k'' are unvoiced, crisp but not aspirated | ||
* | * ''ph'', ''th'', ''kh'', ''ch'', and ''zh'' are aspirated, having a strong burst of breath | ||
=== Vowels === | === Vowels === | ||
A syllable in Taiwanese can't go without having a vowel. [[Media:Seven Tones of Taiwanese.pdf|This chart, ''Seven Tones of Taiwanese'']], shows how to write any vowel in any tone. For now, just look at the basic tone, and the five categories: simple, compound, plus three categories ending in nasals. | |||
==== Single vowels ==== | ==== Single vowels ==== | ||
These are the | These are the {{w|pure vowel}} sounds. | ||
[[File:a, i, u, e, o, ø, m, ng.mp3|thumb|none|Vowels]] | |||
[[File:ma, si, u, e, ho, tø, m, mng.mp3|thumb|none|Examples]] | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! MTL !! Example !! Meaning | ! MTL !! Example !! Meaning | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[a]] || {{ | | [[a]] || {{x|ma}} || also; to scold | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[i]] || {{ | | [[i]] || {{x|si}} || is; yes; ... | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[u]] || {{ | | [[u]] || {{x|u}} || to have | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[e]] || {{ | | [[e]] || {{x|e}} || below; under; ... | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[o]] || {{ | | [[o]] || {{x|ho}} || rain; to give; ... | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[ø]] || {{ | | [[ø]] || {{x|tø}} || at once; ... | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[m]] || {{ | | [[m]] || {{x|m}} || not; will not | ||
|- | |- | ||
| {{ | | {{x|ng}} || {{x|mng}} || to ask | ||
|} | |} | ||
We saw ''m'' earlier as a consonant, but it | * We saw ''m-'' earlier as a consonant, but here it's the vowel. | ||
* In fact, both ''m'' and ''ng'' are complete syllables and complete words. | |||
* We will see -''m'' and -''ng'' as nasal final consonants (NFCs). | |||
==== Compound vowels ==== | ==== Compound vowels ==== | ||
These vowels are a combination of | These vowels are a combination of multiple pure vowel sounds. | ||
[[File:ai, au, ia, iu, iø, iau, ui, oa, oe, oai.mp3]] | |||
[[File:lai, au, ia, siu, biø, liau, ui, toa, hoe, phørhoai.mp3]] | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! MTL !! Example !! Meaning | ! MTL !! Example !! Meaning | ||
|- | |- | ||
| ai | | ai || {{x|lai}} || sharp | ||
|- | |- | ||
| au | | au || {{x|au}} || back | ||
|- | |- | ||
| ia | | ia || {{x|ia}} || to spread | ||
|- | |- | ||
| {{ | | {{x|iu}} || {{x|siu}} || receive; accept; ... | ||
|- | |- | ||
| iø | | iø || {{x|biø}} || temple | ||
|- | |- | ||
| iau | | {{x|iau}} || {{x|liau}} || material/stuff | ||
|- | |- | ||
| ui | | ui || {{x|ui}} || stomach | ||
|- | |- | ||
| oa | | oa || {{x|toa}} || big | ||
|- | |- | ||
| {{ | | {{x|oe}} || {{x|hoe}} || meeting | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | oai || {{x|hoai}} || bad; rotten. see ''{{x|phørhoai}}'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
==== | ==== Vowel plus nasal final consonant ==== | ||
Several vowels can be capped with a nasal final consonant (NFC), either -''m'', -''n'', or -''ng''. | |||
[[File: | [[File:am, im, iam, an, in, un, ien, oan, ang, eng, ong, iang, iong.mp3]] | ||
[[File:lam, akim, liam, ban, kin, tun, lien, goan, bang, teng, gong, liang, iong.mp3]] | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Final !! Example !! Meaning | ||
|- | |||
| {{x|am}} || {{x|lam}} || to mix | |||
|- | |||
| im || {{x|akim}} || aunt | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|iam}} || {{x|liam}} || to nag | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|an}} || {{x|ban}} || slow | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|in}} || {{x|kin}} || near | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|un}} || {{x|tun}} || dull | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ien || {{x|lien}} || to practice | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|oan}} || {{x|goan}} || wish | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ang || {{x|bang}} || dream | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|eng}} || {{x|teng}} || hard | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|ong}} || {{x|gong}} || dumb | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|iang}} || {{x|liang}} || bright | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|iong}} || {{x|iong}} || to use | ||
|} | |} | ||
Some pointers: | |||
* '''ien''' (from '''ia''' + '''n''' = '''ian'''): used to sound like "yan", then "yen", now usually "en" | |||
* '''eng''' (from '''e''' + '''ng'''): used to sound as written, now is a little more like "ieng", but not quite "ing" | |||
==== | ==== Nasal vowels ==== | ||
These vowel sounds are made using your nose. Most vowels from the first two groups can be nasalized, indicated by the letter ''[[v]]'' (read like "you" in English but nasal), chosen because it looks like the Greek letter "nu" ({{wt|ν}}). The word for nose is ''{{x|phvi}}'', which also means "to smell". | |||
[[File: | [[File:Front_nasal_new.mp3]] | ||
[[File:va, hvi, gve, kiaugvo, vai, liengvau, kvia, sviu, gviaw, voa, svoai.mp3]] | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! MTL !! Example !! Meaning | ! MTL !! Example !! Meaning | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | va || {{x|va}} || filling (for dumplings etc.) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|vi}} || {{x|hvi}} || ear | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ve || {{x|gve}} || stiff | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | vo || {{x|kiaugvo}} || proud; arrogant; haughty | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | vai || {{x|vai}} || to carry on back | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | vau || {{x|liengvau}} || lotus root | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|via}} || {{x|kvia}} || classifier for luggage, clothes, events | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | {{x|viu}} || {{x|sviu}} || to think | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | viau || {{x|gviaw}} || itchy. see {{x|gviaugviaw}} (sensation of tickling; ticklish) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | voa || {{x|voa}} || to exchange | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | voai || {{x|svoai}} || mango | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== | === Tones === | ||
Taiwanese is a tonal language which means that pitch is used to convey meaning. Many words are differentiated solely by tone (e.g., all seven tones of ''{{x|si}}''). Learning to speak and hear the [[tones of Taiwanese]] correctly is often difficult for beginners. With practice you will be able to hear and speak them. Again most speakers of Taiwanese are not aware of the different tones but they can all understand you when you pronounce them correctly. | |||
As you may have noticed from the ''Seven Tones'' chart, there are five long tones and two short tones: | |||
* ''f'', ''x'' and ''r'' are silent tone indicators for long tones | |||
* short tones always end with a stop letter that tells both consonant and pitch | |||
[[File:af,_a,_ax,_ar,_aa,_ah,_aq.mp3|thumb|none|{{x|af}}, a, ax, {{x|ar}}, aa, {{x|ah}}, {{x|aq}}]] | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
{| class="wikitable" | ! # !! Tones !! Description !! MTL !! Example !! Animal | ||
! # !! Tones !! Description !! MTL !! Example | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 1 || | | 1 || high || level (55 or 44) || [[f]] (silent) || {{x|khaf}} (''leg''; ''foot'') || {{x|say}} (''lion'') | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 7 || basic || mid-level (33) || default || {{x|toa}} (''big'') || {{x|chviu}} (''elephant'') | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 3 || | | 3 || low falling || somewhat downward (31) || [[x]] (silent) || {{x|khax}} (''to knock'') || {{x|pax}} (''leopard'') | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2 || shouting || sharply downward (51) || [[r]] (silent)|| {{x|ar}} ({{wt|仔}}) || {{x|hor}} (''tiger'') | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5 || curving || mid, downward, up (214) || doubling of vowel || {{x|gaau}} (''extraordinary'') || {{x|hiim}} (''bear'') | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 8 || | | 8 || short high || (5ʔ) || ends with ''h'', ''p'', ''t'' or ''k'' || {{x|ah}} (''a box'') || {{x|lok}} (''deer'') | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 4 || | | 4 || short low || (3ʔ) || ends with ''q'', ''b'', ''d'' or ''g'' || {{x|aq}} (''a duck'') || {{x|piq}} (''snapping turtle'') | ||
|} | |} | ||
[[File:say, chviu, pax, hor, hiim, lok, piq.mp3|thumb|none|say, chviu, pax, hor, hiim, lok, piq]] | |||
==== Short tones ==== | |||
Let's look at the [[short tones]] first: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Pitch !! -h !! -p !! -t !! -k | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 8. high || {{x|ciah}} (''to eat'') || {{x|zap}} (''ten'') || {{x|lat}} (''strength'') || {{x|hak}} (''study'') | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 4. low || {{x|phaq}} (''to hit'') || {{x|ciab}} (''juice'') || {{x|pad}} (''eight'') || {{x|kag}} (''horn'') | ||
|} | |||
* high short tones end with ''h'' ({{w|glottal stop}}), ''p'', ''t'' and ''k'', which are stops sounding similar to how they're used as an initial consonant | |||
* low short tones end with ''q'', ''b'', ''d'', and ''g'', which are the same stops as above, but signal the vowel is low pitch | |||
* ''{{x|iet}}'' and ''{{x|ek}}'', the short tones of ''ien'' and ''eng'', may sound more like ''et'' and ''iek'' | |||
| | ==== Long tones ==== | ||
Here are some common examples of the [[long tone]]s: | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
! Tone !! Example !! Meaning | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1. high || {{x|ciaf}} || here | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 7. basic || {{x|si}} || is | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3. low-falling || {{x|khix}} || to go | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2. shouting || {{x|goar}} || I; me | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5. curving || {{x|ee}} || possessive particle | ||
|} | |} | ||
The tone indicators always come to the right of the vowel, with one exception. To indicate the curving tone of a compound vowel, double the ''a'' if present, or else the last vowel letter. For example: ''{{x|cviaa}}'', ''{{x|laai}}'', ''{{x|ngg}}''. | |||
[[ | ===== Special vowels ===== | ||
For certain vowels in certain tones, some ornamental substitutions/shortcuts are used. Refer to the [[Media:Seven Tones of Taiwanese.pdf|''Seven Tones'']] chart. | |||
* '''{{x|y}}''', '''{{x|w}}''': [[high tone]] of '''i''' and '''u''' | |||
* '''{{x|ie}}''', '''{{x|uo}}''', '''{{x|ea}}''': [[shouting tone]] of '''i''', '''u''', '''e''' | |||
* '''{{x|ae}}''', '''{{x|ao}}''': shortcuts for "a + ie" and "a + uo" | |||
* '''{{x|øo}}''': shortcut for "øø" | |||
* None of these apply with NFCs except: '''{{x|ym}}''', '''{{x|yn}}''', '''{{x|wn}}''' | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! Syll. Tail !! Shortcut !! Example || Meaning | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | if, ifm, ifn || {{x|y}}, {{x|ym}}, {{x|yn}} || {{x|ty}}, {{x|kym}}, {{x|cyn}} || pig, gold, very | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | uf, ufn || {{x|w}}, {{x|wn}} || {{x|titw}}, {{x|zhwn}} || spider, springtime | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ir || {{x|ie}} || {{x|lie}} || you; ... | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ur || {{x|uo}} || {{x|kuo}} || (''of time'') long | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | er || {{x|ea}} || {{x|boea}} || tail | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | air || {{x|ae}} || {{x|hae}} || sea | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | aur || {{x|ao}} || {{x|kao}} || dog. nine | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | øø || {{x|øo}} || {{x|kiøo}} || bridge; eggplant | ||
|} | |} | ||
==== Tone sandhi | === Syllable structure === | ||
[[File:Tone | A syllable in Taiwanese is either: | ||
* [initial] + '''vowel''' + [nasal final consonant] | |||
* [initial] + [v] + '''vowel''' | |||
Anything in square brackets is optional. This means: | |||
* a vowel is always required | |||
* ''v'', ''-m'', ''-n'', and ''-ng'' are mutually exclusive | |||
Also, we almost never find more than one nasal: | |||
* e.g. ''{{x|man}}'' and ''{{x|mang}}'' don't exist (but ''{{x|ban}}'' and ''{{x|bang}}'' do exist) | |||
* the only exceptions are the various tones of ''{{x|mng}}'' and ''{{x|nng}}'' | |||
== Tone sandhi == | |||
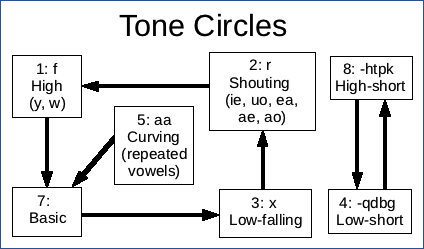
[[File:Tone Circles.png|right|frame|The seven tones, and how they change due to tone sandhi.]] | |||
The basic unit of speech is the syllable, which can change tone depending on | The basic unit of speech is the syllable, which can change tone depending on its environment. This process is generally called [[tone sandhi]] ("sandhi" is from the Sanskrit word for "joining") and in Taiwanese the rules for it are extensive. | ||
Generally, a syllable inside of a word changes tone according to the Tone Circles. For example, the single-syllable word for "duck" (bird): ''{{x|aq}}''. Its original tone is low-short. After adding the suffix ''{{x|ar}}'', the tone becomes high-short: ''{{x|ah'ar}}''. | |||
More examples: | |||
* ''jit'' (sun) + ''thaau'' (head) = ''{{x|jidthaau}}'' (the sun) | |||
* ''cit'' (one) + ''sud'' (a bit) + ''ar'' = ''{{x|cidsut'ar}}'' (a little amount of something) | |||
Inside a sentence, the last syllable of most nouns don't change tone. But if that noun is actually used as an adjective, it will. For example, in ''cidsut'ar {{x|png}}'' (a bit of rice), the ''ar'' changes to high tone when spoken. Furthermore, in ''{{x|ciah}} cidsut'ar png'', the verb ''ciah'' (to eat) changes to low-short tone when spoken. | |||
You may have realized by now that tone change is connected to grammar. These tone changes are probably by far the hardest part of learning Taiwanese. | |||
== Special punctuation marks == | |||
=== Apostrophe (') === | |||
When two syllables are put together, sometimes one letter might appear to be connected to the right syllable when it shouldn't be. The [[apostrophe]] is used to remove the ambiguity. For example: | |||
* {{x|of}} (烏; "black") + {{x|kix}} (痣; "mole") = o'kix = {{x|okix}} | |||
* {{x|og}} (惡; "evil") + {{x|ix}} (意; "intention") = {{x|ok'ix}} | |||
In MTL, we group the letters starting from the right into the longest syllable. So reading ''okix'', the second syllable is ''kix''. Then the first syllable is ''o''. There's no need to write ''o'kix''. | |||
If you drop the apostrophe from ''ok'ix'', it would be ''okix'', so the apostrophe needs to stay. | |||
=== Hyphen (-) === | |||
When reading | A hyphen is used to join two, or more isolated words to | ||
before the hyphen | make a new compound word with its own meaning. When reading a hyphenated word, the syllable just before the hyphen should change tone. For example: {{XL|Taioaan}} + laang = {{XL|Taioaan-laang}} (Taiwanese person) | ||
[[File:Taioaan, Taioaan-laang.mp3]] | |||
The last syllable of ''Taioaan'' changes tone when spoken, so the compound word sounds like ''Taioanlaang''. | |||
=== | === Backquote (`) === | ||
When a word contains a [[ | When a word contains a [[backquote]], all the syllables after | ||
it are accented in a weaker, lower tone -- either a low-falling tone | it are accented in a weaker, lower tone -- either a low-falling tone | ||
or a low stop. The tone of the syllable before the | or a low stop. The tone of the syllable before the backquote remains unchanged. | ||
Example: | Example: | ||
* [[File:Kviaf`sie. | * [[File:Kviaf`sie.mp3]] {{x|kviaf`sie}} ((v.) ''to freak someone out'') - ''kviaf'' keeps its high tone but ''sie'' is pronounced with a weakened low tone. | ||
* [[File:Kviasie. | * [[File:Kviasie.mp3]] {{x|kviasie}} ((adj.) ''scared of death'') – ''kviaf'' is pronounced with normal tone change from high to basic while ''sie'' is pronounced as a shouting tone. ''{{w|Kiasi}}'' is Hokkien phrase that describes the attitude of being overly afraid or timid. | ||
== | == Next steps == | ||
* [[Greeting Phrases in Taiwanese]] | |||
* [[Practical Taiwanese Conversation]] | * [[Practical Taiwanese Conversation]] | ||
* [[Taiwanese | * [[Introduction to Taiwanese Vocabulary]] | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
* [ | * [https://learntaiwanese.org/Beginner's%20Guide%20to%20Taiwanese.html ''A Beginner's Guide to Taiwanese''], version 1.0: 2017 | ||
* [https://wdcts.org/ WDCTS] - MLT Introduction, Useful Handout, Videos & References. (in Chinese) | |||
* Modern Literal Taiwanese Foundation (MLTF). [https://learntaiwanese.org/english/mtl.html Modern Literal Taiwanese (MLT) Handbook] | |||
* {{Textbook_1990}} | |||
[[Category:Getting started]] | [[Category:Getting started]] | ||
[[Category:Modern Literal Taiwanese]] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:11, 14 January 2025
Li hø! Taiwanese is a beautiful and musical language spoken in Taiwan and by Taiwanese people around the world. This Beginner's Guide to Taiwanese will provide you with a brief introduction to the spoken language as well as a system for writing Taiwanese called Modern Literal Taiwanese (MLT), also known as "Modern Taiwanese Language" (MTL).
Most speakers of Taiwanese aren't aware that there are several writing systems for the language. Pe̍h-ōe-jī (POJ), also known as Church Romanization, might be the most popular romanization, though the government is now promoting a similar system called Tâi-lô. We're going to use MTL here because we found it very useful while studying Taiwanese at the Washington DC Taiwanese School, and we think it could help you too. True, most Taiwanese speakers won't be able to read any of these systems, but they will probably understand you better because you learned one.
How to make a syllable
Let's learn how to write any syllable using the MLT alphabet. The three important parts of a syllable we will look at first are: starting consonant, vowel, and ending consonant. We will talk about tones later.
Initial consonants
A syllable can start with one of 18 initial consonants. Some sounds have an approximation in English, while others may be more exotic. For now, you can just ignore the silent indicators (mainly f, x, r, v).
| MTL | Approx. | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| p | spin | papaf | father |
| ph | pin | phaq | to hit |
| m | Mimi | mi | noodle |
| b | mumble | baq | meat |
| t | stem | tit | straight |
| th | Thomas | theh | to take |
| n | neat | nii | year |
| l | lima | laang | person |
| k | ski | kaf | to add |
| kh | key | khix | to go |
| h | heap | hii | fish |
| g | gaggle | go | five |
| c(i) | gee | ciaf | here |
| ch(i) | cheese | chiaf | car |
| s | she / saw | si | is; yes |
| j | vision / zeta | jit | sun; day |
| z | yards | zef | this |
| zh | Tsai (Ts'ai) | zhaix | vegetable |
The p vs. b and k vs. g may be hard to differentiate at first. They are part of a three-way distinction, going from muddy to plain to aspirated.
- b and g are voiced: the vocal cords vibrate along with the consonant
- p, t, k are unvoiced, crisp but not aspirated
- ph, th, kh, ch, and zh are aspirated, having a strong burst of breath
Vowels
A syllable in Taiwanese can't go without having a vowel. This chart, Seven Tones of Taiwanese, shows how to write any vowel in any tone. For now, just look at the basic tone, and the five categories: simple, compound, plus three categories ending in nasals.
Single vowels
These are the pure vowel sounds.
| MTL | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| a | ma | also; to scold |
| i | si | is; yes; ... |
| u | u | to have |
| e | e | below; under; ... |
| o | ho | rain; to give; ... |
| ø | tø | at once; ... |
| m | m | not; will not |
| ng | mng | to ask |
- We saw m- earlier as a consonant, but here it's the vowel.
- In fact, both m and ng are complete syllables and complete words.
- We will see -m and -ng as nasal final consonants (NFCs).
Compound vowels
These vowels are a combination of multiple pure vowel sounds.
| MTL | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| ai | lai | sharp |
| au | au | back |
| ia | ia | to spread |
| iu | siu | receive; accept; ... |
| iø | biø | temple |
| iau | liau | material/stuff |
| ui | ui | stomach |
| oa | toa | big |
| oe | hoe | meeting |
| oai | hoai | bad; rotten. see phørhoai |
Vowel plus nasal final consonant
Several vowels can be capped with a nasal final consonant (NFC), either -m, -n, or -ng.
| Final | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| am | lam | to mix |
| im | akim | aunt |
| iam | liam | to nag |
| an | ban | slow |
| in | kin | near |
| un | tun | dull |
| ien | lien | to practice |
| oan | goan | wish |
| ang | bang | dream |
| eng | teng | hard |
| ong | gong | dumb |
| iang | liang | bright |
| iong | iong | to use |
Some pointers:
- ien (from ia + n = ian): used to sound like "yan", then "yen", now usually "en"
- eng (from e + ng): used to sound as written, now is a little more like "ieng", but not quite "ing"
Nasal vowels
These vowel sounds are made using your nose. Most vowels from the first two groups can be nasalized, indicated by the letter v (read like "you" in English but nasal), chosen because it looks like the Greek letter "nu" (ν). The word for nose is phvi, which also means "to smell".
| MTL | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| va | va | filling (for dumplings etc.) |
| vi | hvi | ear |
| ve | gve | stiff |
| vo | kiaugvo | proud; arrogant; haughty |
| vai | vai | to carry on back |
| vau | liengvau | lotus root |
| via | kvia | classifier for luggage, clothes, events |
| viu | sviu | to think |
| viau | gviaw | itchy. see gviaugviaw (sensation of tickling; ticklish) |
| voa | voa | to exchange |
| voai | svoai | mango |
Tones
Taiwanese is a tonal language which means that pitch is used to convey meaning. Many words are differentiated solely by tone (e.g., all seven tones of si). Learning to speak and hear the tones of Taiwanese correctly is often difficult for beginners. With practice you will be able to hear and speak them. Again most speakers of Taiwanese are not aware of the different tones but they can all understand you when you pronounce them correctly.
As you may have noticed from the Seven Tones chart, there are five long tones and two short tones:
- f, x and r are silent tone indicators for long tones
- short tones always end with a stop letter that tells both consonant and pitch
| # | Tones | Description | MTL | Example | Animal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | high | level (55 or 44) | f (silent) | khaf (leg; foot) | say (lion) |
| 7 | basic | mid-level (33) | default | toa (big) | chviu (elephant) |
| 3 | low falling | somewhat downward (31) | x (silent) | khax (to knock) | pax (leopard) |
| 2 | shouting | sharply downward (51) | r (silent) | ar (仔) | hor (tiger) |
| 5 | curving | mid, downward, up (214) | doubling of vowel | gaau (extraordinary) | hiim (bear) |
| 8 | short high | (5ʔ) | ends with h, p, t or k | ah (a box) | lok (deer) |
| 4 | short low | (3ʔ) | ends with q, b, d or g | aq (a duck) | piq (snapping turtle) |
Short tones
Let's look at the short tones first:
| Pitch | -h | -p | -t | -k |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8. high | ciah (to eat) | zap (ten) | lat (strength) | hak (study) |
| 4. low | phaq (to hit) | ciab (juice) | pad (eight) | kag (horn) |
- high short tones end with h (glottal stop), p, t and k, which are stops sounding similar to how they're used as an initial consonant
- low short tones end with q, b, d, and g, which are the same stops as above, but signal the vowel is low pitch
- iet and ek, the short tones of ien and eng, may sound more like et and iek
Long tones
Here are some common examples of the long tones:
| Tone | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 1. high | ciaf | here |
| 7. basic | si | is |
| 3. low-falling | khix | to go |
| 2. shouting | goar | I; me |
| 5. curving | ee | possessive particle |
The tone indicators always come to the right of the vowel, with one exception. To indicate the curving tone of a compound vowel, double the a if present, or else the last vowel letter. For example: cviaa, laai, ngg.
Special vowels
For certain vowels in certain tones, some ornamental substitutions/shortcuts are used. Refer to the Seven Tones chart.
- y, w: high tone of i and u
- ie, uo, ea: shouting tone of i, u, e
- ae, ao: shortcuts for "a + ie" and "a + uo"
- øo: shortcut for "øø"
- None of these apply with NFCs except: ym, yn, wn
| Syll. Tail | Shortcut | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| if, ifm, ifn | y, ym, yn | ty, kym, cyn | pig, gold, very |
| uf, ufn | w, wn | titw, zhwn | spider, springtime |
| ir | ie | lie | you; ... |
| ur | uo | kuo | (of time) long |
| er | ea | boea | tail |
| air | ae | hae | sea |
| aur | ao | kao | dog. nine |
| øø | øo | kiøo | bridge; eggplant |
Syllable structure
A syllable in Taiwanese is either:
- [initial] + vowel + [nasal final consonant]
- [initial] + [v] + vowel
Anything in square brackets is optional. This means:
- a vowel is always required
- v, -m, -n, and -ng are mutually exclusive
Also, we almost never find more than one nasal:
- e.g. man and mang don't exist (but ban and bang do exist)
- the only exceptions are the various tones of mng and nng
Tone sandhi
The basic unit of speech is the syllable, which can change tone depending on its environment. This process is generally called tone sandhi ("sandhi" is from the Sanskrit word for "joining") and in Taiwanese the rules for it are extensive.
Generally, a syllable inside of a word changes tone according to the Tone Circles. For example, the single-syllable word for "duck" (bird): aq. Its original tone is low-short. After adding the suffix ar, the tone becomes high-short: ah'ar.
More examples:
- jit (sun) + thaau (head) = jidthaau (the sun)
- cit (one) + sud (a bit) + ar = cidsut'ar (a little amount of something)
Inside a sentence, the last syllable of most nouns don't change tone. But if that noun is actually used as an adjective, it will. For example, in cidsut'ar png (a bit of rice), the ar changes to high tone when spoken. Furthermore, in ciah cidsut'ar png, the verb ciah (to eat) changes to low-short tone when spoken.
You may have realized by now that tone change is connected to grammar. These tone changes are probably by far the hardest part of learning Taiwanese.
Special punctuation marks
Apostrophe (')
When two syllables are put together, sometimes one letter might appear to be connected to the right syllable when it shouldn't be. The apostrophe is used to remove the ambiguity. For example:
In MTL, we group the letters starting from the right into the longest syllable. So reading okix, the second syllable is kix. Then the first syllable is o. There's no need to write o'kix.
If you drop the apostrophe from ok'ix, it would be okix, so the apostrophe needs to stay.
Hyphen (-)
A hyphen is used to join two, or more isolated words to make a new compound word with its own meaning. When reading a hyphenated word, the syllable just before the hyphen should change tone. For example: Taioaan + laang = Taioaan-laang (Taiwanese person) The last syllable of Taioaan changes tone when spoken, so the compound word sounds like Taioanlaang.
Backquote (`)
When a word contains a backquote, all the syllables after it are accented in a weaker, lower tone -- either a low-falling tone or a low stop. The tone of the syllable before the backquote remains unchanged.
Example:
- kviaf`sie ((v.) to freak someone out) - kviaf keeps its high tone but sie is pronounced with a weakened low tone.
- kviasie ((adj.) scared of death) – kviaf is pronounced with normal tone change from high to basic while sie is pronounced as a shouting tone. Kiasi is Hokkien phrase that describes the attitude of being overly afraid or timid.
Next steps
External links
- A Beginner's Guide to Taiwanese, version 1.0: 2017
- WDCTS - MLT Introduction, Useful Handout, Videos & References. (in Chinese)
- Modern Literal Taiwanese Foundation (MLTF). Modern Literal Taiwanese (MLT) Handbook
- Liim Keahioong (1990). Textbook of Modern Literal Taiwanese. Tainan, Taiwan: Ta-hsia Press.